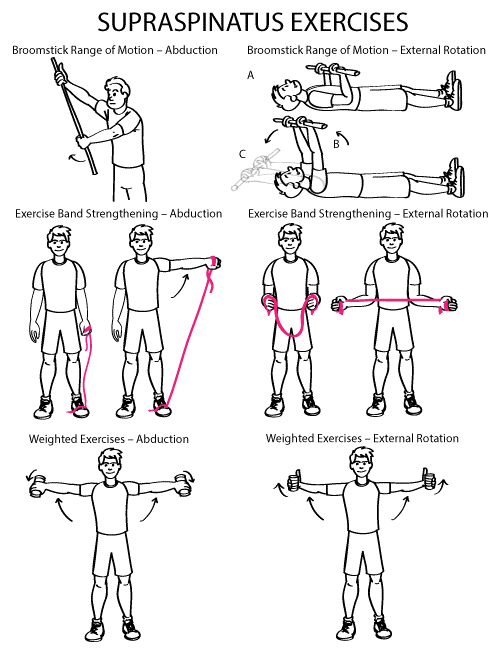DEFINITION:
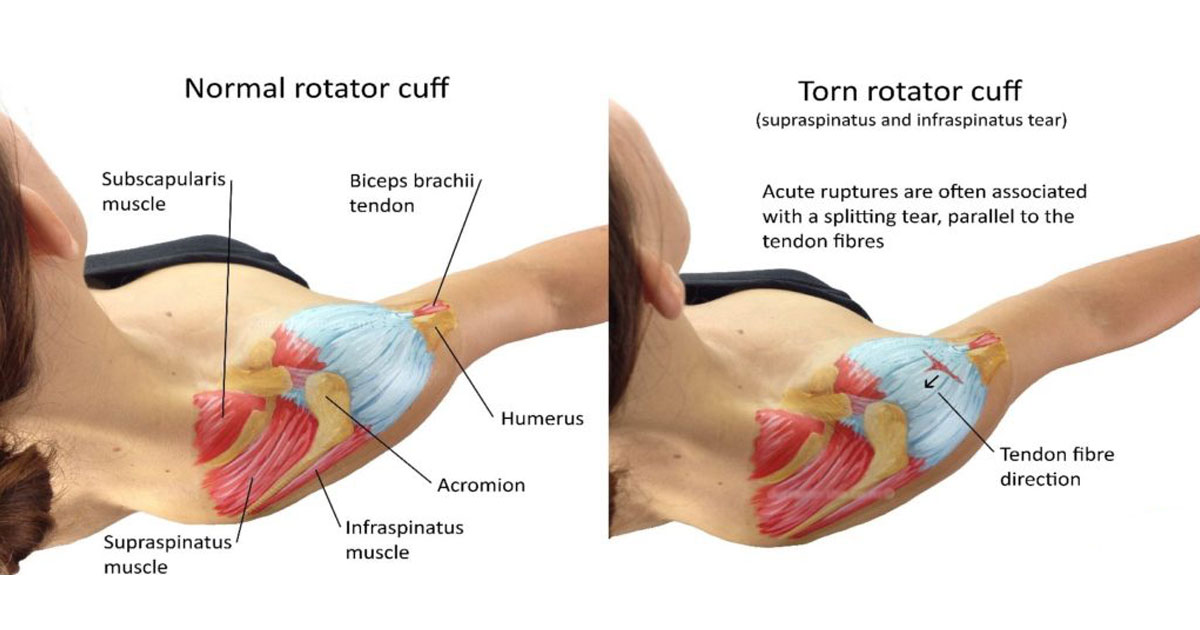
Rotator cuff injuries are a common cause of shoulder pain in people of all age groups. The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles that help move and stabilize the shoulder joint
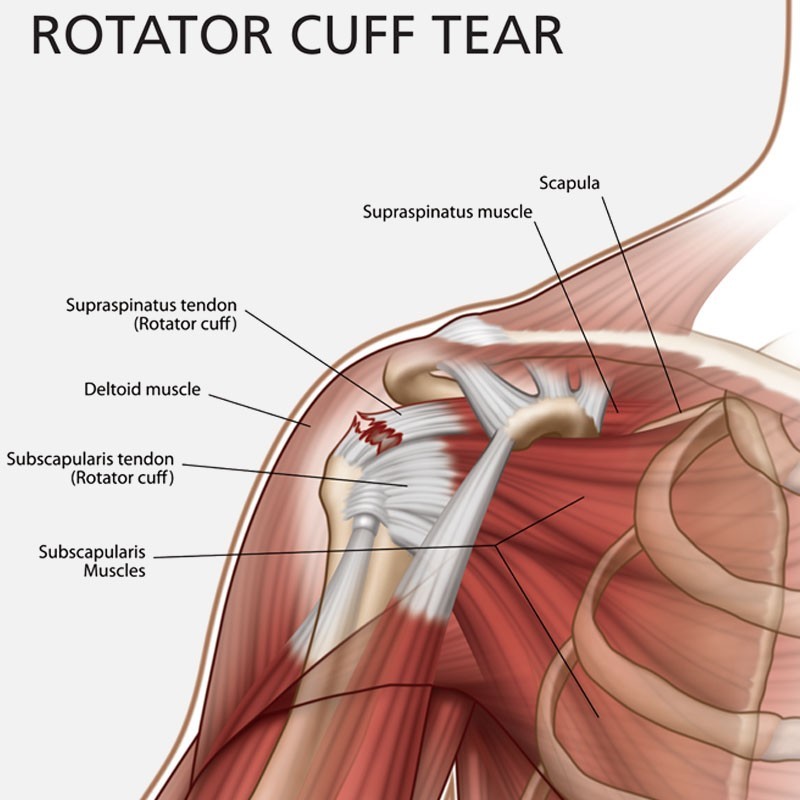
Damage to any or all of the four muscles and the ligaments can occur because of acute injury, chronic overuse, or gradual aging
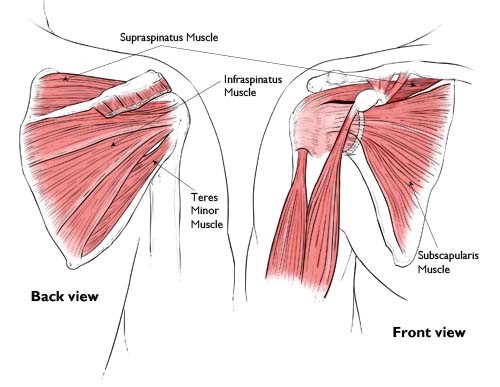
The FOUR ROTATOR CUFF MUSCLES are:
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Subscapularis
- Teres minor
EPIDEMIOLOGY
- Full-thickness rotator cuff tears are present in approximately 25% of individuals in their 60s and 50% of individuals in their 80s.
- Full-thickness rotator cuff tears without symptoms are common and present in approximately 50% of patients over age 65
- Symptomatic full-thickness tears progress in tear size in approximately 50% of cases at an average of 2 years
CAUSES:
- H/o of repetitive overhead activities(throwing a ball, racquet sports)
- Trauma(fall/accident)
- Age-related degeneration
- Occupation related injury
- Chronic lifting
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS:
- Pain and swelling in the front of the shoulder and side of the arm
- Clicking sound when raising the arm
- Weakness in the shoulder
- Night pain
- Decreased range of motion of the shoulder and strength in the affected arm because of muscle spasm &pain
- Large tears may cause the inability abduct the arm (raise it away from the side of the body) due to significant pain and loss of muscle power
- Feeling of instability
TREATMENT:
1.IMAGING STUDIES:
- X –ray findings usually are normal in rotator cuff injury
- MRI helps identify all the structures that make up the rotator cuff, degeneration changes, partial or complete tears of tendons and muscles or combination of alA
2.MEDICATIONS:
- Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen may help decrease the pain and swelling of the injury
- Steroid injections into the shoulder joint may be helpful.
3.PHYSIOTHERAPY:
- The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and restore function
- After initial rest, cold packs & passive ROM exercises can be started
- Alternate heat and cold therapy may be beneficial for some patients
- Range of motion exercises like assistive & active exercises are helpful in maintaining shoulder function
- Once the acute stage is over, resistance exercises using Thera bands can begin as long as they are done in pain free range
- A sling may help support the arm & rest the rotator cuff muscles, however long-term use of a sling causes significant stiffening of the shoulder joint
4.SURGERY:
- Patients with extensive tears of the rotator cuff tendon or muscle.
- If conservative treatment of rest, ice, exercises and other treatments is not having the desired effect after 6 weeks
- Professional sports people
- If your job requires constant shoulder use then surgery for a severe injury may be preferable
- Activity requiring constant shoulder use ,surgery may be preferable
5.PROGNOSIS:
- Conservative treatment has a 40-90% success rate
- Surgery often has good results, with some studies citing a 94% satisfaction rate with the surgery, however older people take longer to heal.
- Patients with extensive tears of the rotator cuff tendon or muscle.
- If conservative treatment of rest, ice, exercises and other treatments is not having the desired effect after 6 weeks
- Professional sports people
- If your job requires constant shoulder use then surgery for a severe injury may be preferable
- Activity requiring constant shoulder use ,surgery may be preferable